Android, But Not Yours: Companies Locking Down the System
EditorialThursday, 30 October 2025 at 14:03

Android has always been the big open alternative to Apple’s locked-down ecosystem. Due to its Linux-based nature, it was almost a limitless OS. Despite the way that Google delivered it to us, we could easily tweak it. Thanks to the open nature of Android devices, it was easy to unlock bootloaders and install custom ROMs, or dive deep into their settings to make your phone truly yours.
At least, that was the initial idea. Today, tell us a different story, and the reality is much more complicated. Both Google and device manufacturers have slowly but steadily tightened control over Android devices (cough... cough... Xiaomi), making the “open” system feel a lot more like a polished cage.
Manufacturers and Google Are Tightening Control
For years, enthusiasts could unlock bootloaders, install custom firmware, and even modify core system functions. It was a playground for curious minds and developers. That freedom came at a cost, of course, because tampering with the system could break your device or void warranties. But at least the option was there. Nowadays, unlocking a phone is harder than ever. Some brands, like Samsung with Knox or Huawei with heavy restrictions, make unlocking a device almost impossible without risking permanent damage. Xiaomi, once popular among modders for its flexible approach, now limits bootloader unlocks and closely monitors system modifications.

Security is the most common justification. Manufacturers claim these restrictions protect users from malware, accidental damage, and other risks. To some extent, they are right. Modern Android phones store more personal data than ever, and preventing unauthorized modifications can prevent some serious security breaches. But the problem is that security often becomes a convenient excuse to control what users can do with their own devices. The trade-off is clear: safety at the expense of freedom. Users lose flexibility, innovation suffers, and the vibrant modding community that once thrived on Android is shrinking.
Read also
Android’s Original Promise
- Linux-based, open-source system offering near-limitless customization.
- Users could unlock bootloaders, install custom ROMs, tweak settings, and truly own their device.
- A vibrant modding and developer community thrived on this openness.
Manufacturer Restrictions
- Companies like Samsung (Knox), Huawei, and Xiaomi increasingly limit bootloader unlocking.
- System modifications are closely monitored; unlocking can void warranties or damage devices.
- Security is the main justification, but it often doubles as a way to control users.
Google is Taking Away Android's Freedom
Unfortunately, Google is not innocent in this story. While Android is technically open-source, the ecosystem around Google services has enormous influence. Phones that do not comply with Google’s certification rules can lose access to essential apps like Gmail, Maps, and the Play Store. This puts manufacturers in a position where they have to enforce Google’s rules to keep their devices functional for most users.

Yes, I've used Google Gemini to create this image— Ironic, right?
Google also controls updates through mechanisms like Project Treble and Play Services, which, while streamlining updates, limit end users' control over when and how their devices receive patches. In practice, your phone may be “Android,” but your control over it is heavily filtered through Google’s and the manufacturer’s rules. If you unlock the bootloader or make deep changes, you may not pass Google Play certification, and some important apps, like banking apps or even WhatsApp, may not work properly.
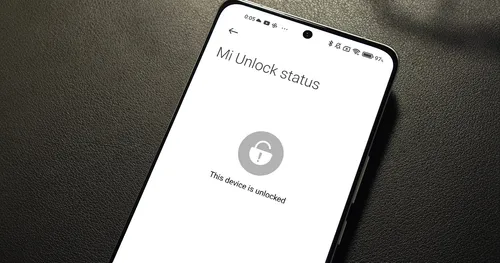
Why Google's Recent Policies Feel Controlling
- Updates are now mediated through Google Play Services and the system framework.
- Your device may receive updates automatically or on a schedule determined by the manufacturer.
- If you unlock your bootloader or install a custom ROM, you may break compatibility updates, which can block OTA updates or Google Play certification. You lose the ability to install important apps like bank apps or even simple messengers like WhatsApp. Even contactless payments can stop working in rooted or unlocked devices.
Impact on Users and the Android Ecosystem
The impact on users goes beyond annoyance. Repairability and device longevity will suffer. Once a phone stops receiving official updates, you are left with limited options. Rooting and installing custom ROMs was once the go-to solution for extending a device’s life. Now, however, it has become difficult and risky. Privacy can also take a hit. Locked systems often limit what apps you can control, which data you can manage, and how freely you can secure your own information. For those who value independence over convenience, it is a frustrating reality.
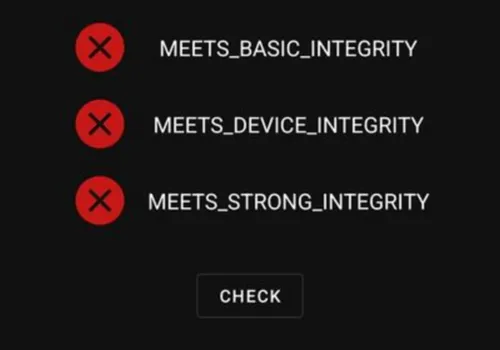
If your device loses integrity, several apps will stop working properly. That happens often in unlocked bootloaders and needs extra work from custom ROM developers.
Despite this, alternatives exist. Custom ROMs like LineageOS still offer a path to freedom, but they require patience and technical knowledge. The challenge is that fewer people are willing or able to navigate these hurdles, which means the ecosystem of unlocked, user-controlled Android devices is slowly shrinking.
Looking Ahead: Will Android Remain Free?
Android was supposed to be the free playground of mobile technology, the system where users were in charge. Now, it feels like that freedom is increasingly symbolic. The smartphone OEMs and Google have erected invisible walls around the system, limiting what you can modify and how long your device remains flexible.

The question is whether Android will continue to honor its promise of freedom, or if it will eventually join Apple in a world where your device is only as open as the company allows. For anyone who remembers the early days of Android, that is a question worth asking.
Popular News
Latest News
Loading