In a world where the internet keeps advancing and we become more reliant on digital things, the security of data has become one of the main concerns of the current era. Nowadays, we hold sensitive data like banking info and emails on our smartphones. The malicious agents keep advancing their methods to steal data and get access to sensitive information. Therefore, tech companies are working hard to improve the security of their products. Microsoft is no exception and has been working hard to make Windows more secure. The Operating System is one of the most used worldwide PCs, so it is also one of the biggest targets for hackers. Windows 11 brought big advancements in terms of security, and these advancements left some users out of this update.
According to Microsoft, the high system requirements that prevented users with fairly new computers from installing Windows 11 are mainly due to security features. So, if Windows 11 is crafted with security as one of its top priorities, what we can do to benefit from this? In this article, we will guide you on how to improve security and privacy with Windows 11.
Windows 11 And Its Focus on Security
Many of the Windows 11 system requirements have been out for years with Windows 10. However, only people related to corporate IT departments were aware of them, or at least paid attention to them. Some of these features won’t be enabled automatically if you update from Windows 10. They will be enabled on all new computers sold directly with Windows 11. Some are very sensible and don’t affect your computer’s performance. Others can hurt the overall performance.
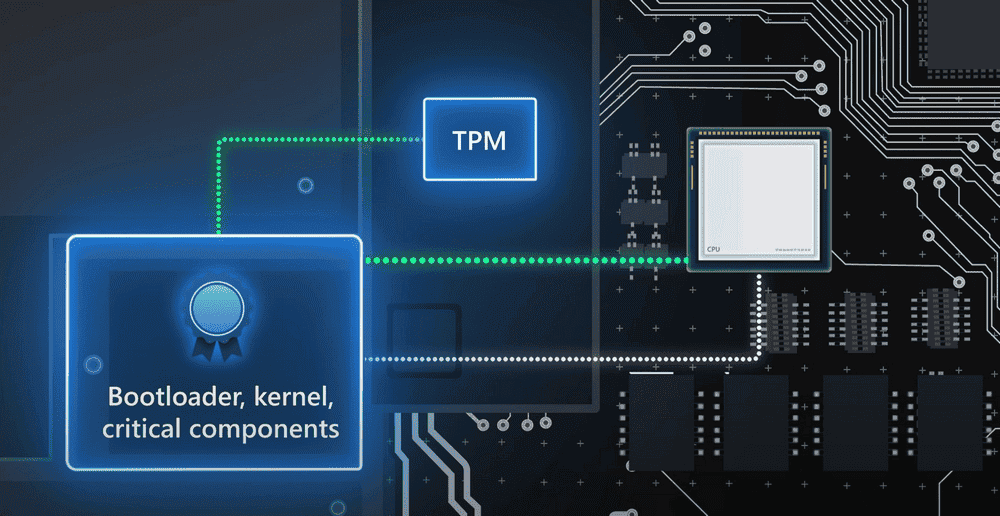
Secure Boot and TPM
To install Windows 11 on your PC, you will need a modern processor (Intel 8th Generation or Newer / AMD Ryzen 3000 or newer) and two security features: Secure Boot and Trusted Platform Module, the so-called TPM.
Secure Boot has been available for many years. However, most of the users haven’t had it running because it was an option, and mostly felt like an unnecessary hassle. The feature is part of UEFI, the modern replacement for BIOS. It allows the computer’s basic software to detect and stop a modified operating system by checking its cryptographic signatures.
Enabling Secure Boot effectively stops sneaky malware that, for example, installs itself under Windows as a so-called bootkit and can covertly read everything that happens on the system. You can enable Secure Boot in your computer’s BIOS settings. Activating it is not a requirement for running Windows 11. The real requirement is for the computer to be able to use Secure Boot.
Trusted Platform Module
TPM, on the other hand, is a requirement for even installing and running the new System. There are ways to overcome this limitation, like for example, using Rufus to build a flashable USB. However, Microsoft warns that unofficial support means you won’t get future updates.
TPM is, in fact, a good security feature. The basic functions of TPM are the secure storage of encryption keys and certificates. It also ensures the creation of secure creation and control of new keys. For example, it could be the encryption key for Bitlocker that secures all data on your hard drive or the encryption key used with Windows Hello for quick login with PIN or Facial Recognition. Third-party apps like Firefox and Chrome also use TPM if it’s present, even in Windows 10.
With TPM enabled, Windows and individual programs that need to generate encryption keys can ask the TPM to do so. The generated keys are only stored there and can never be extracted or copied to other locations. This brings way more security than keys generated by the regular processor. After all, some malware or trojans can intercept these keys.
If you’re hit by malware with a keylogger that captures everything you type on your keyboard, this includes your PIN. However, because the PIN is linked to an encryption key on the particular computer, the malware creators will not be able to log in to your Microsoft.
Virtualization-Based Security
One of the features that limits Windows 11 from being installed on older hardware is something called virtualization-based security or VBS. This means that the system uses the ability of modern processors to run code in virtual machines with their separate parts of working memory.
This feature was first used to run other OS inside Windows or another system that allows you to test software or run a program made for other platforms. A common is Mac users, that can run Windows with a virtual machine for Windows-specific programs. The same principle applies to Windows 11’s ability to run Android.
Virtualization-based security uses the same techniques to separate certain parts of Windows. Therefore, other parts of the system cannot access them. It consists of several different components.
Memory Integrity
Another feature that improves security on Windows 11 is the memory integrity. You can enable it via Windows Security and select Device Security. If VBS is active, you will see a green tick next to Core isolation and it says “Virtualization-based security protects the core parts of your device”.
- Click on Core Isolation Information
- You’ll be taken to a submenu where you can enable or disable Memory Integrity.
This is one of the features powered by VBS. It means that Windows places sensitive code in a virtual machine (VM). This VM is isolated from the regular system, so it cannot be easily accessed, even with admin permissions. This increases security and protects against malware. The downside? It sacrifices performance.
Unfortunately, enabling Memory Integrity costs 25% of some machines’ performance. This is a relevant number for those who need all the power of the computer. Therefore, gamers or users who use the computer for intensive work often choose to disable the feature despite its security benefits.
Privacy Protection
One of the most criticized aspects of Windows 10 was its native behavior of sending analytics data to the company. This was an issue for most users, and the worst aspect was that it was difficult to turn off this feature. Another criticized point was how the Start Menu was full of ads.
In Windows 11, Microsoft listened to the criticism and adapted. For that reason, there are more Privacy Protection features. User data sharing has been significantly improved.
The Settings for both Windows itself and the authorization for third-party apps to access features such as the camera and your image library are located in Settings >> Privacy & Security. Here is how to use them and turn off any sharing you don’t want.
Gizchina News of the week
The settings panel has three major sections: Security, Windows Permissions, and App Permissions. Security is mostly a shortcut to the separate program Windows Security.
Windows Permissions
General is an important setting for the advertising ID, the unique code that, if you allow it, can be used to track you. Advertise buyers can trace a purchase of a product to an advertising banner you’ve clicked on. You can turn this off to avoid data tracking.
Inking and Typing Personalization
If you use a pen and sometimes write directly on the screen, this feature lets you decide whether Windows will be able to create a custom dictionary for you.
Speech
Diagnostics & Feedback
Here you will find the settings for how you use the computer. It can also be used for analytical purposes. The data is anonymized and it’s intended to help Microsoft improve Windows and other products. The system sends data. You can choose to send additional data. It is a requirement if you want to connect your computer to the Windows Insider Program.
Activity History
It is a feature of your Microsoft account. It allows you to continue what you have done on one device while sitting at another that is logged in to the same account. If you have only one computer, you can turn it off.
Search Permissions
This menu brings two important settings. You can enable filter for adult content in the Windows search function and you can also enable or disable search history.
Search in Windows
Has other settings for the search function. Here you can tweak which folders should or not be searched. The menu also allows you to set Windows Search to look for files outside your home folder.
App Permissions
There are multiple sub-sections for everything on your computer related to privacy. The most important ones are conveniently located at the top of the app permissions section: Location, which deals with whether Windows and apps can find out where you are. Camera and Microphone are there as well as voice activation and even access to send you notifications.
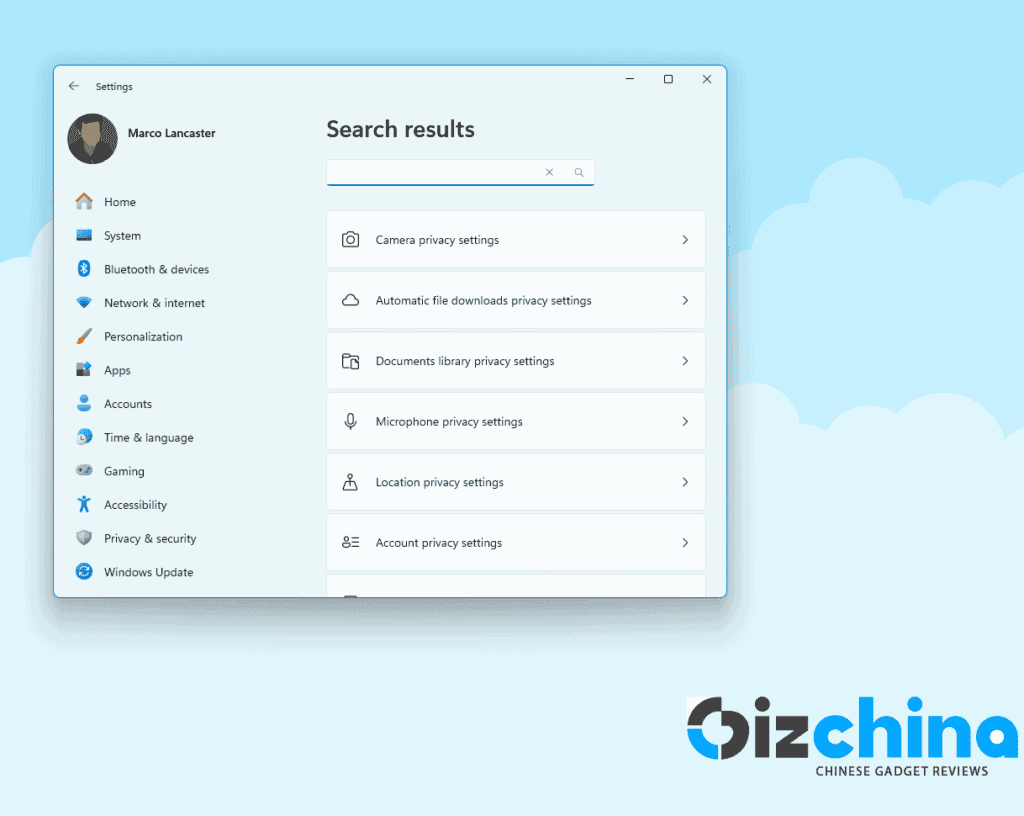
Under Camera and Microphone, you can turn off or on access to individual applications. You can disable permissions for apps that you no longer use. The fewer programs have access the better.
Location Data is not as useful as it is on a smartphone. For some users, the only benefit of having it enabled is that online stores can easily display your nearest physical store. If that isn’t something important, you can switch off location tracking.
Other Settings You Can Use to Improve Security on Windows 11
In addition to settings in Privacy and Security, there are a bunch of other settings you can customize to improve your privacy while using Windows.
Disable Device Usage
Microsoft wants to know how you use Windows 11. For that reason, there is a feature called Device Usage. Microsoft uses it to customize the system and give you advertising that makes sense to you. If you don’t want your usage to be tracked you can easily turn it off.
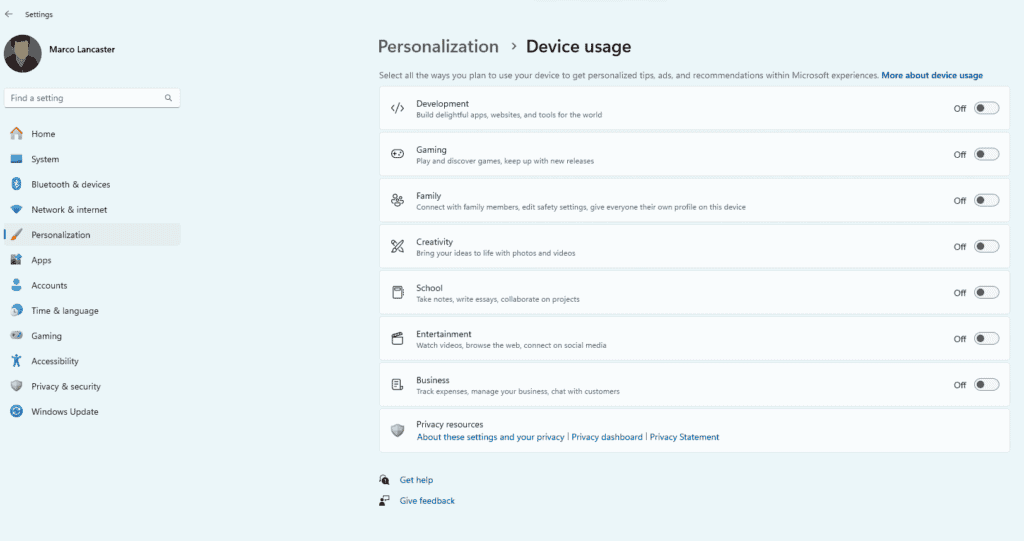
- Open Settings, Personalization and Go to Device Usage. Put everything in Off if you don’t want to supply this info to Microsoft.
Adjust your Microsoft Account on your Privacy Panel
To get full access to your Microsoft account’s privacy you can tweak the settings on Privacy Panel via the web browser.
Head to account.microsoft.com/privacy and sign in with your Microsoft account. At the top, you can select Get Started for a wizard that will guide you through the settings. You can also select Manage your Activity Data to make changes manually.
Get Control Over Programs
You can also tweak and get more control over products like Xbox or Microsoft Teams.
Open your Microsoft’s privacy panel and select “Privacy Settings in our Products.”
Do Not Share The Clipboard
Microsoft offers an advanced cloud clipboard manager with Windows 11. It allows you to save the clipboards of all your devices and allows you to synchronize them in a common clipboard list. It’s a useful feature, however, some users may be impacted by the fact that your data is being sent to a server. Thankfully, it can be disabled. To disable it follow these steps:
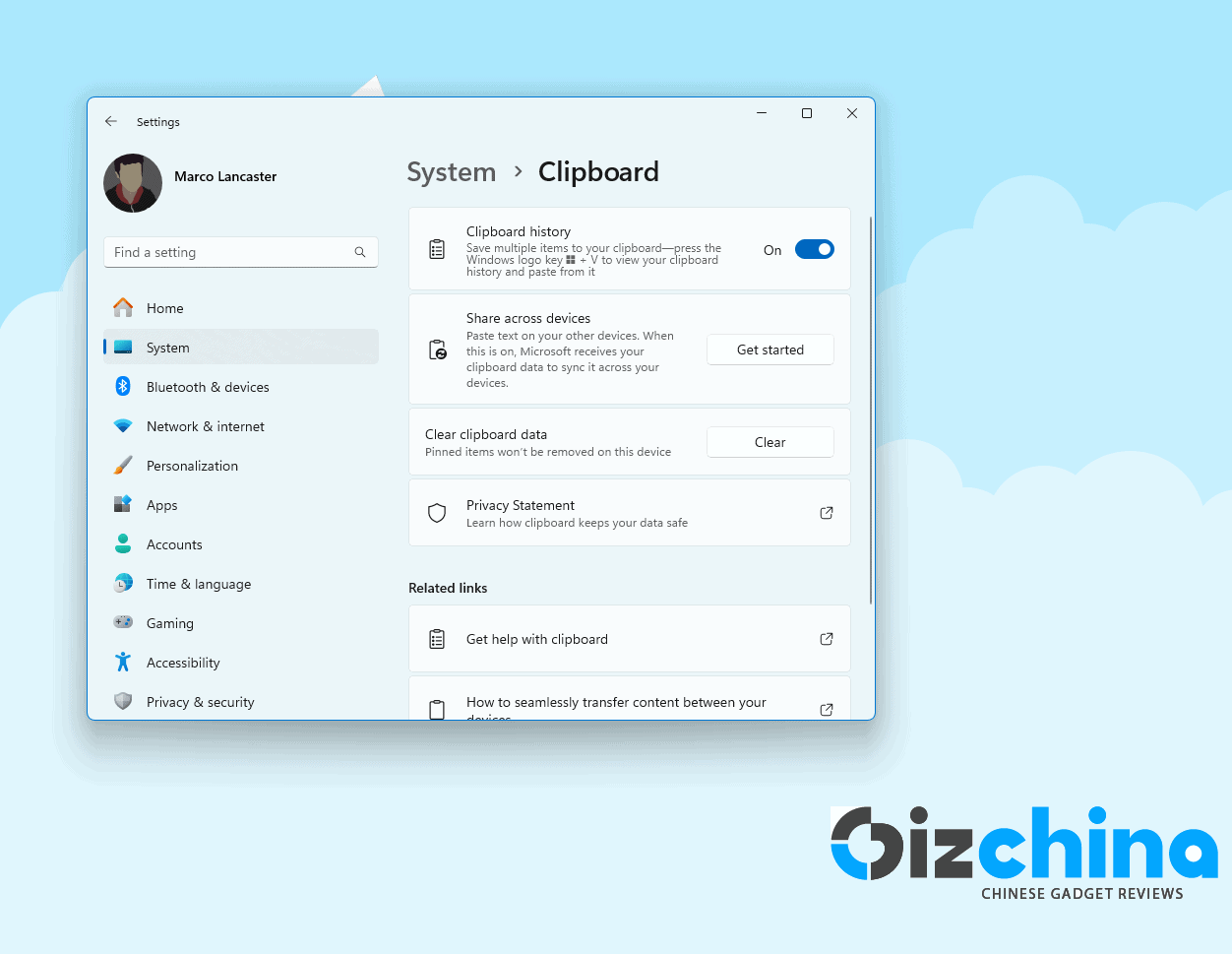
- Open Settings >> System >> Clipboard.
- Switch off the Clipboard History or choose to not Synchronize clips between devices. You can also select Clear to delete the history in the cloud.
Hide what you’ve done
Windows can show, for convenience, the documents and other things you’ve opened recently. If this is an issue for you, you can still disable the feature. Hence, if other people use your computer they won’t be able to check what you’ve been doing.
- Open Settings and Select Personalization, Start. Here switch off the Feature Show Recently Opened items.
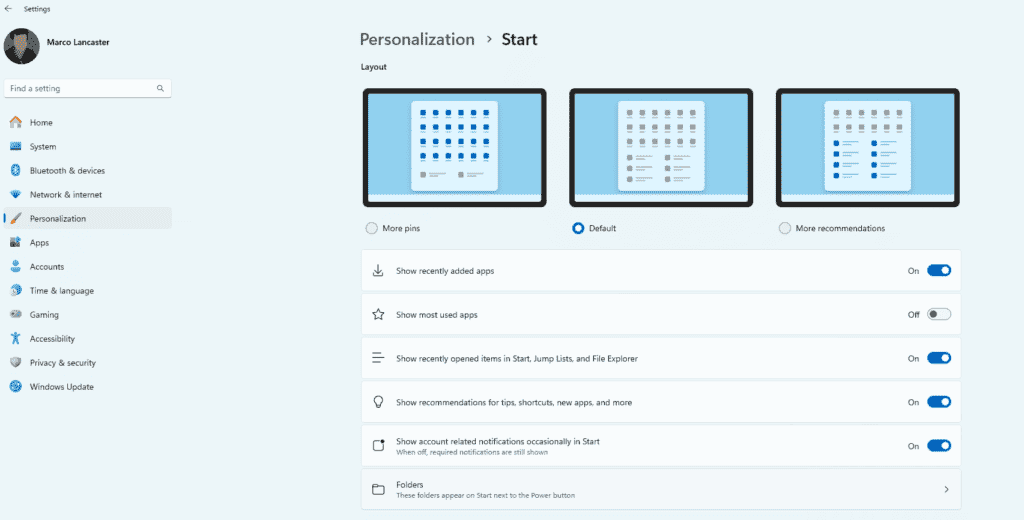
There are more options you can adjust in this setting.
Stop Sharing Between Devices
A new feature in Windows deals with synchronizing software settings and other data between different computers. If you have a desktop and a laptop, this feature can be handy. However, if you have just one computer, you’re sending data to the cloud for no reason. Disabling it is quite simple.

- Open Settings and Select Apps, Advanced App Settings. Tap on Share Across Devices and switch off the feature or choose how to use it.
Conclusion
As you’ve learned in this article, Microsoft made a lot of adjustments to make Windows 11 more secure. At the same time, it is quite versatile in terms of privacy. After all, users can disable most of the data tracking features, to keep their devices secure and private.
Special Credit to PCWorld, and PCforalla.se as the original article was written in Swedish.





